Portfolio
What to include?⎹ Where to publish?⎹ How to publish your portfolio on GitHub Pages
What to include?
Anything that makes you proud and attests to your skills, for example:
- Manuals, tutorials, and other documentation projects
- Non-technical texts on field-related topics (articles, reviews)
- Graphic design projects (infographics, diagrams)
- Content created with different tools
- Content published in different formats
- Open-source contributions
Where to publish?
Attaching projects to emails can be awkward, if not impossible (file size limits). Ideally, you should collect all your works in one place and publish them online. Then you just include the link on your resume.
First, you will need a hosting service to upload your resources. If you have a blog or a website where you can store and share your files – and you know how to – that’s an option. If you’d rather follow a simple method with few technicalities, read on.
How to publish your portfolio on GitHub Pages
GitHub is a cloud-based development platform that provides repository hosting services and user interface for Git. For many IT specialists, it is also the default go-to service for showcasing their projects to the world.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to publish your portfolio on GitHub. You will first upload your files to the server and then deploy your projects as fully-working websites hosted on GitHub Pages.
When you publish your portfolio on GitHub, your recruiters will see the end result of your work as well as the code behind your projects. You will also show that you know about version control systems and static site generators.
PREREQUISITES:
- Basic knowledge of Git, GitHub, and static site generators.
- At least one valid document in a web format: HTML or Markdown.
- A user account set up on GitHub.
- GitHub Desktop installed on your computer.
Creating a GitHub repository
- Sign in to your account at github.com.
-
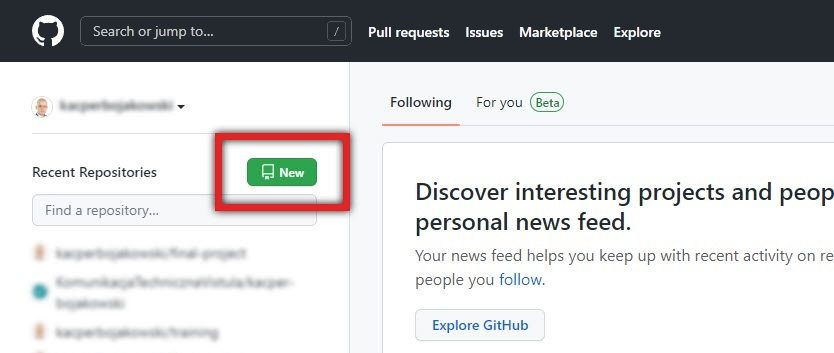
Next to Recent repositories click New.
-
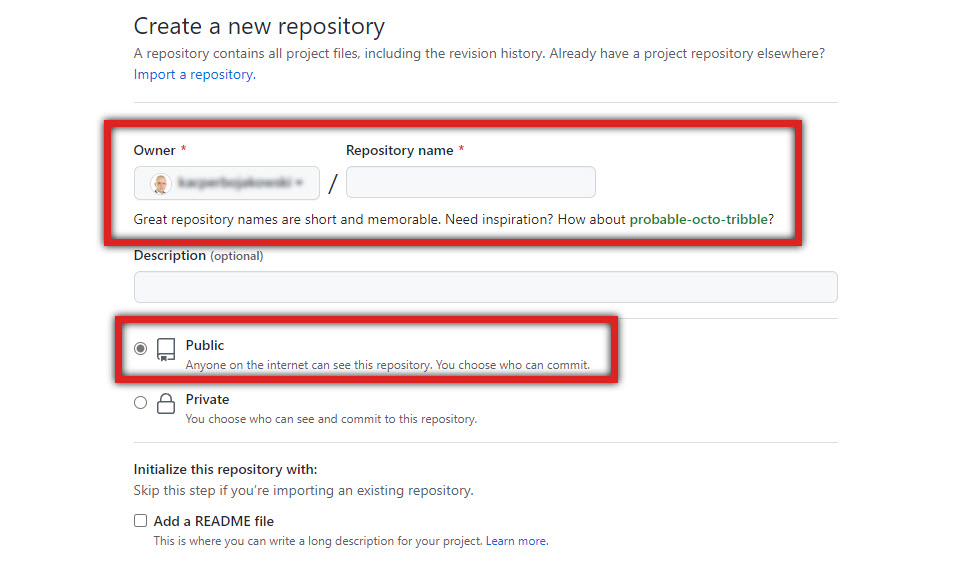
Write your repository name and make sure it’s set to Public.
-
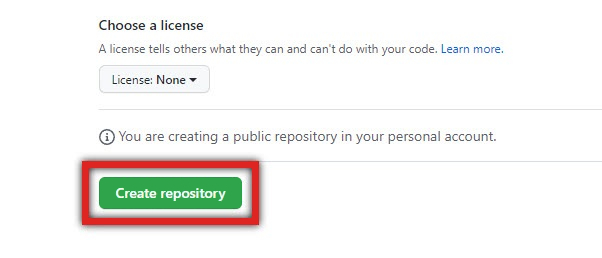
Click Create repository at the bottom.
Adding files to the repository
- Rename your document as “index”, so that your file is
index.md(for Markdown) orindex.html(for HTML). - Open GitHub Desktop.
-
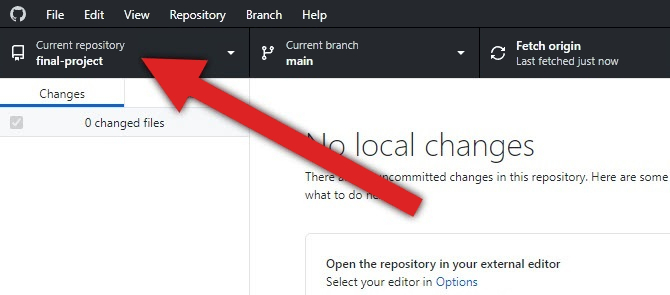
Click Current repository.
-
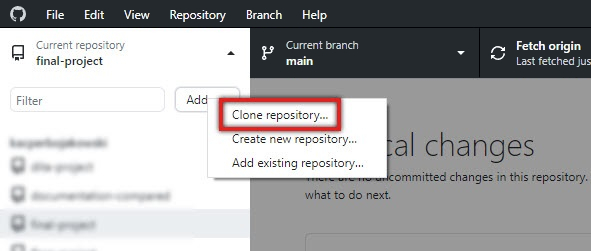
Click Add and choose Clone repository….
-
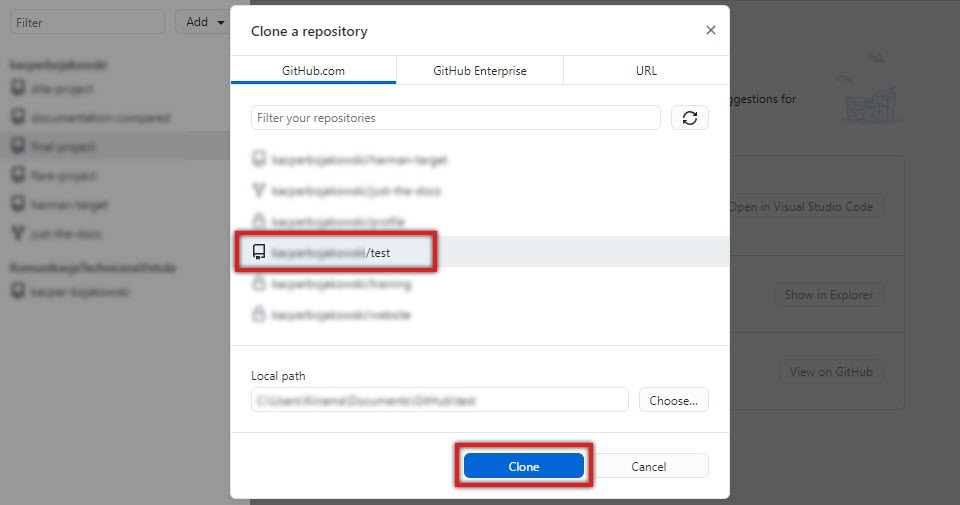
Find the repository you created earlier, select it, and click Clone.
-
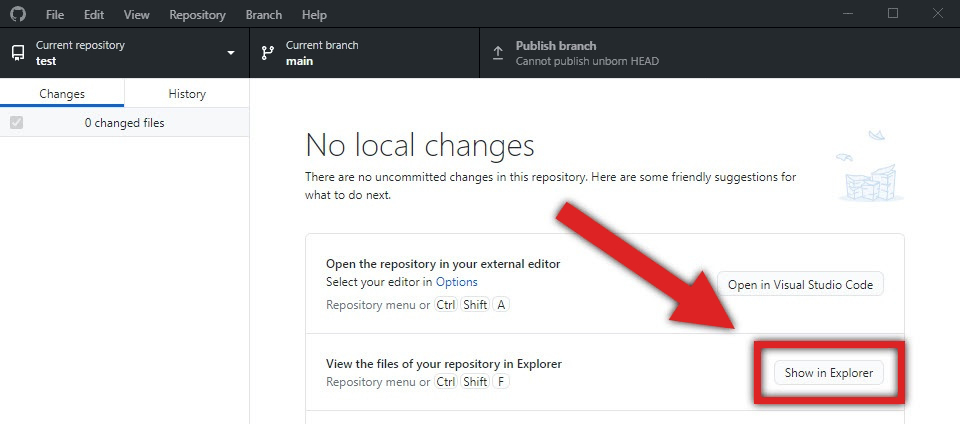
Click Show in Explorer to view the local folder for your repository.
- Copy your document and paste it in this folder.
-
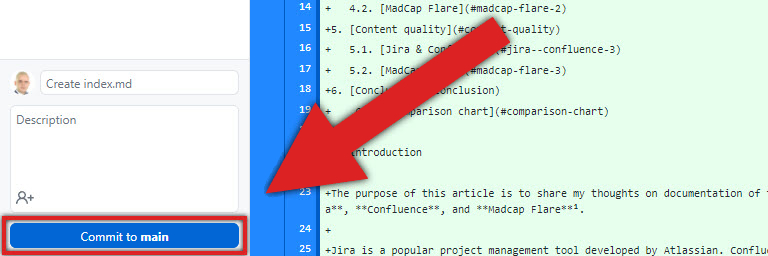
Go back to the GitHub Desktop window and click Commit to main.
-
Click Publish this branch.
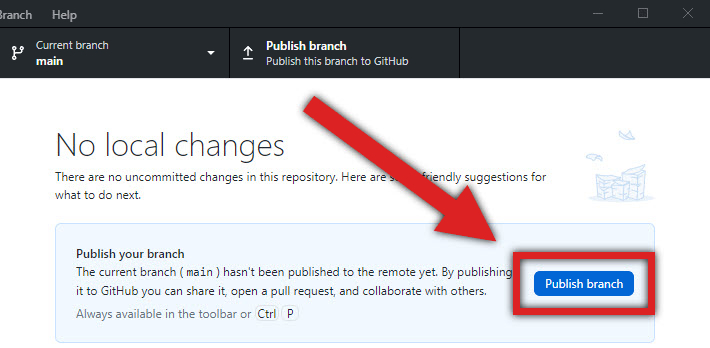
-
Open your browser, go to your account on github.com, and check your repository. It should already contain the file you added.
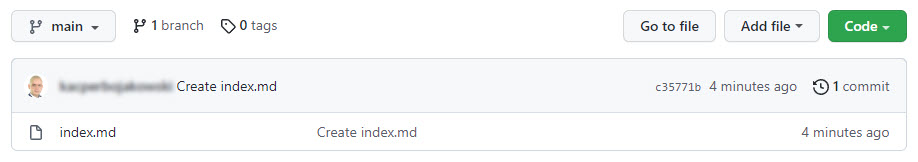
Publishing on GitHub Pages
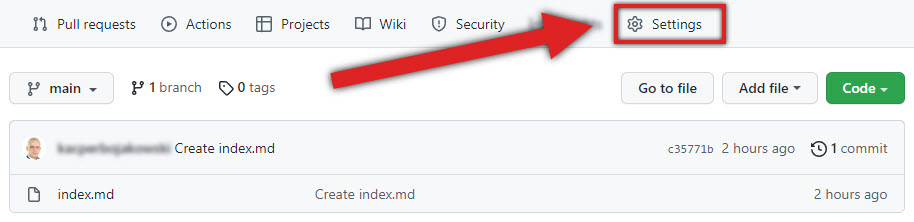
-
On your repository page, click Settings.
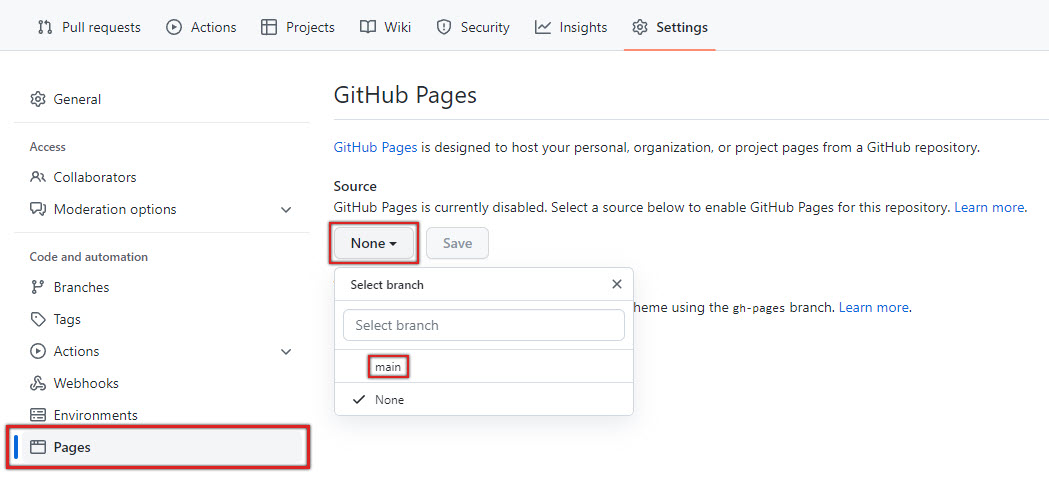
- Go to Pages and find the Source tab.
-
Click None and change it to branch main.
-
Click Save.

You will see the information that your page is ready to be published:
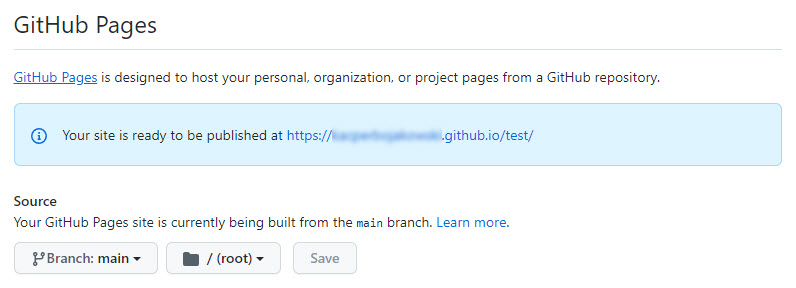
This is the address of your project published on GitHub Pages.
You won’t be able to view it right away. It will take some time until the link actually works.
Your page will go through three stages, each represented by one of these icons respectively:

-
Click github-pages under the Environments tab on your repository page. If you don’t see it, wait a few minutes and refresh the page.
-
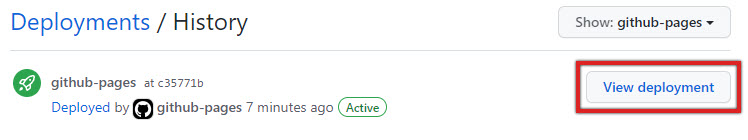
Once your page is Active, click View deployment to see it.
Organizing your portfolio
Pin your repository
- Go to github.com and sign in.
- Click your avatar in the top-right corner and select Your profile.
- Click Customize your pins.
- Choose the repository you want to pin. You can have a maximum of 6 pinned repositories on your profile page.
Add the link and description
- Open your repository page.
- Next to About, click the cog icon.

- In the Description field, add a description of your project; it will appear together with your pinned repository on your profile page.
- In the Website field, add the address of your project published on GitHub Pages.
Done!
That’s it! Now you can share your GitHub portfolio. The address is https://github.com/ followed by your user name, e.g., https://github.com/john-smith/.
🖊️ NOTE: There are more ways to add your project to GitHub, for example via file upload on the GitHub website or through Git command line interface. The method described here is just very universal; it is a middle ground between difficulty and ability to conveniently add multiple files at once.
Troubleshooting
I renamed my file to “index.md”/”index.html”, but it doesn’t save with the new extension.
Indeed, when you rename, for example, a TXT file to “index.md”, you might simply end up with a TXT file named “index.md”, as in index.md.txt. To make sure there are no problems, save your document via Visual Studio Code. Open your file in VSC, and then click File → Save As… and choose the right extension under Save as type.
I don’t see options for setting source under Settings → Pages.
Make sure your repository is set to Public and not Private. Go to: Settings → scroll all the way down → Danger Zone tab → click Change visibility; accept your change, go back to Pages, and see if the option appears.
I made changes in my project but they don’t show on my Page.
Wait a few more minutes and refresh the page. Pages can take a while to update. Sometimes you may need to restart your browser or delete it’s temporary files. Also, make sure that you have commited and pushed your changes in GitHub Desktop.
Can I include non-web formats, such as PDF documents, in my portfolio ?
Absolutely! To have PDF documents show up on a GitHub Page, place them in the same repository as your page and refer to them via Markdown’s relative-path links, e.g., [My PDF](myfile.pdf).
Next topic: Resume